Embark on a journey through the world of building envelopes with our guide on 'Building Envelope Explained: What It Is and Why It Matters'. Discover the crucial role these structures play in construction and why they are essential for energy efficiency and maintenance savings.
Introduction to Building Envelope

The building envelope is the physical separator between the interior and exterior environments of a building. It consists of all the elements that protect the building from the outside elements and help maintain a comfortable and healthy indoor environment.
Primary Functions of Building Envelope
- Weatherproofing: The building envelope prevents water, wind, and other weather elements from entering the building, protecting it from damage.
- Thermal Insulation: It helps regulate the temperature inside the building by reducing heat transfer, thus increasing energy efficiency.
- Air Barrier: The envelope controls the airflow in and out of the building, improving indoor air quality and preventing drafts.
- Vapor Retarder: It manages moisture levels within the building, preventing condensation and mold growth.
Components of Building Envelope
- Exterior Walls: These walls provide structural support and protection from the weather.
- Roof: The roof covers the top of the building, preventing water infiltration and heat loss.
- Windows and Doors: These openings in the envelope allow natural light and ventilation while providing security and insulation.
- Foundation: The foundation forms the base of the building, supporting the structure and preventing moisture from seeping in.
Importance of Building Envelope
![What is Building Envelope? A Simple Definition [+Solutions] What is Building Envelope? A Simple Definition [+Solutions]](https://interior.suarananggroe.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/building-envelope-defined.jpg)
The building envelope plays a crucial role in the construction industry by serving as the barrier between the interior and exterior environments of a building. It not only protects the structure from external elements but also significantly impacts energy efficiency and maintenance costs.
Impact on Energy Efficiency
The design and quality of the building envelope directly affect the energy consumption of a building. A well-insulated envelope with proper sealing can minimize heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer, reducing the need for heating and cooling systems.
This results in lower energy bills and a smaller carbon footprint, making the building more sustainable in the long run.
Reduction in Maintenance Costs
By preventing moisture infiltration and air leakage, a well-designed building envelope can help avoid issues like mold growth, rot, and structural damage. This proactive approach to building envelope design can lead to lower maintenance costs over time, as the building is better protected against wear and tear caused by weather conditions.
Components of Building Envelope
Building envelope is made up of several key components that work together to ensure the structural integrity and energy efficiency of a building. Each component plays a vital role in protecting the interior environment from external elements such as wind, rain, and temperature fluctuations.
Let's delve into the different elements that constitute the building envelope and understand the significance of each component.
Walls
Walls are one of the most crucial components of the building envelope. They provide structural support and act as a barrier against moisture, air infiltration, and heat loss. Common materials used for wall construction include concrete, brick, wood, and steel.
Insulation is often added within the walls to enhance energy efficiency and thermal performance.
Roof
The roof is another essential component of the building envelope, serving as protection against weather elements such as rain, snow, and sunlight. Roofing materials like asphalt shingles, metal panels, and clay tiles are commonly used to ensure durability and water resistance.
Adequate insulation in the roof helps in maintaining consistent indoor temperatures and reducing energy costs.
Windows
Windows not only allow natural light and ventilation into the building but also impact energy efficiency. Energy-efficient windows are typically double or triple glazed with low-emissivity coatings to minimize heat transfer. Materials like vinyl, wood, aluminum, and fiberglass are commonly used for window frames to provide both functionality and aesthetics.
Doors
Doors play a dual role in the building envelope by providing security and regulating access while also contributing to energy conservation. Insulated doors with weather-stripping prevent air leakage and maintain indoor comfort levels. Materials such as wood, steel, fiberglass, and aluminum are popular choices for durable and energy-efficient door construction.
Foundation
The foundation forms the base of the building envelope, supporting the entire structure and protecting it from moisture intrusion. Common foundation materials include concrete, stone, and brick, with waterproofing techniques applied to prevent water seepage. Proper foundation design and construction are essential for ensuring the stability and longevity of the building.
Design Considerations for Building Envelope
When designing a building envelope, several key factors need to be taken into consideration to ensure the overall performance and efficiency of the structure. Design choices play a crucial role in determining how well the building envelope can protect the interior space from external elements and maintain a comfortable indoor environment.
Here are some essential considerations to keep in mind:
Material Selection
- Choose materials that offer good insulation properties to minimize heat loss or gain.
- Consider the durability and resistance of materials to weather conditions and moisture infiltration.
- Opt for sustainable materials that are eco-friendly and energy-efficient.
Sealing and Air Tightness
- Ensure proper sealing of joints and connections to prevent air leakage and improve energy efficiency.
- Incorporate air barriers to reduce drafts and enhance indoor comfort levels.
- Implement air tightness testing to identify and address any leaks in the building envelope.
Orientation and Shading
- Optimize building orientation to maximize natural light exposure and minimize heat gain.
- Utilize shading devices such as overhangs, louvers, or awnings to control solar heat gain during peak hours.
- Consider the impact of landscaping and external features on the building envelope's performance.
Ventilation and Moisture Control
- Design adequate ventilation systems to ensure proper air circulation and moisture control within the building envelope.
- Integrate moisture barriers and vapor retarders to prevent condensation and mold growth.
- Consider the climate conditions of the location to tailor ventilation and moisture control strategies accordingly.
Final Thoughts
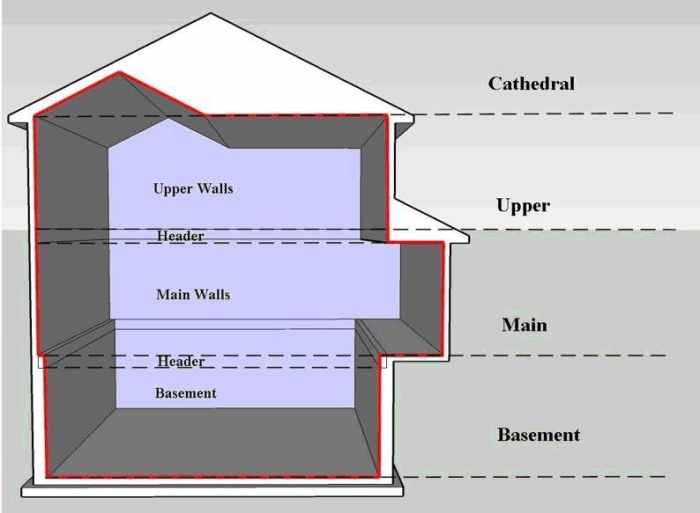
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of building envelopes is vital for anyone involved in the construction industry. From their components to design considerations, the impact of a well-designed building envelope cannot be overstated.
FAQ Corner
What are the primary functions of a building envelope?
The building envelope serves as a barrier between the interior and exterior environments, providing protection against elements like weather and moisture infiltration.
How does the building envelope impact energy efficiency?
A well-insulated building envelope can minimize heat loss or gain, reducing the need for heating or cooling systems and ultimately saving energy.
What materials are commonly used in building envelope construction?
Materials like concrete, steel, wood, glass, and various insulation types are frequently used in building envelope construction.