Embarking on the journey of Building Envelope Enhancements That Save Energy, we delve into a world where architectural innovation meets sustainability, paving the way for a greener future. This guide aims to shed light on the crucial role of building envelopes in energy efficiency and how enhancements in this area can lead to significant savings.
As we explore the various aspects of building envelope enhancements, from materials to design considerations, we uncover the key strategies for creating energy-efficient structures that not only reduce environmental impact but also cut down on costs.
Understanding Building Envelope Enhancements
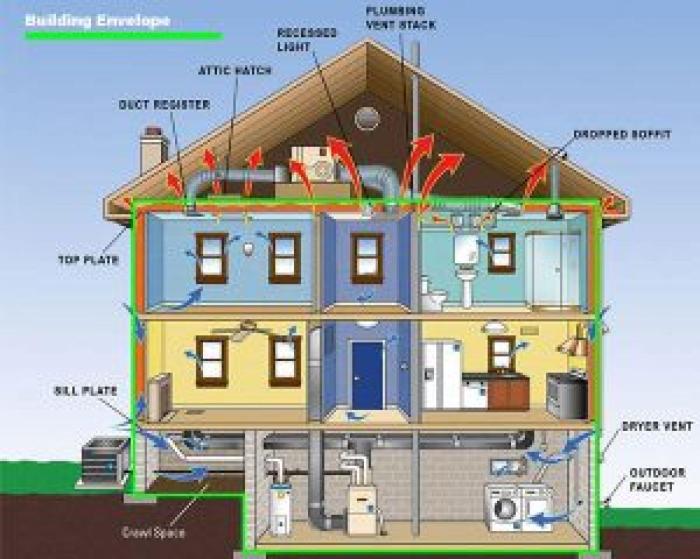
Building envelope enhancements refer to improvements made to the exterior components of a building, such as walls, windows, roofs, and foundations, to increase energy efficiency and reduce energy consumption.
The building envelope plays a crucial role in energy efficiency as it acts as the physical barrier between the interior and exterior of a building. A well-designed and properly sealed building envelope can prevent heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer, reducing the need for heating, cooling, and ventilation systems to work harder.
Importance of Building Envelope Enhancements
- Improved Insulation: Upgrading insulation in walls, roofs, and floors can reduce heat transfer, maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature without excessive reliance on heating or cooling systems.
- Air Sealing: Sealing gaps and cracks in the building envelope prevents air leakage, enhancing indoor air quality and reducing the energy needed to maintain consistent temperatures.
- High-Performance Windows: Installing energy-efficient windows with low-E coatings and insulating frames can minimize heat transfer and reduce the demand for artificial heating and cooling.
- Solar Reflective Roofing: Using cool roofing materials that reflect sunlight can decrease roof temperatures, lowering cooling loads and energy consumption.
Types of Building Envelope Enhancements
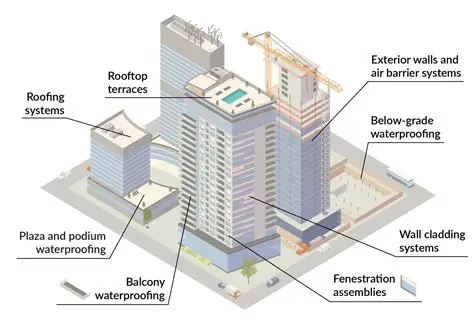
Insulation, high-performance windows, and air sealing are common types of building envelope enhancements that play a crucial role in improving energy efficiency and comfort within a building.
Insulation
Insulation is a key component of the building envelope that helps regulate indoor temperatures by reducing heat transfer through walls, ceilings, and floors. By minimizing heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer, insulation can significantly lower energy consumption and improve overall comfort levels within a building.
High-Performance Windows
Incorporating high-performance windows into the building envelope can provide numerous benefits such as improved insulation, reduced air leakage, and enhanced natural light and views. These windows are designed with advanced materials and technologies to minimize heat transfer, block harmful UV rays, and enhance sound insulation, ultimately contributing to energy savings and occupant comfort.
Materials for Building Envelope Enhancements
Building envelope enhancements rely on a variety of materials to improve energy efficiency and sustainability in buildings. These materials play a crucial role in reducing heat loss, preventing air leakage, and enhancing overall building performance.
Spray Foam Insulation
Spray foam insulation is a popular choice for building envelope enhancements due to its high R-value, which measures the insulation's effectiveness. This material provides an airtight seal, minimizing heat transfer and reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling. Furthermore, spray foam insulation can fill gaps and cracks in walls and roofs, creating a more efficient building envelope.
Double-Glazed Windows
Double-glazed windows consist of two panes of glass separated by a layer of gas, typically argon or krypton. This design improves insulation and reduces heat transfer, making double-glazed windows an energy-efficient choice for building envelope enhancements. By minimizing heat loss and gain, these windows help maintain stable indoor temperatures and reduce the reliance on heating and cooling systems.
Weather-Resistant Barriers
Weather-resistant barriers are essential components of building envelope enhancements, providing protection against moisture infiltration and air leakage. These barriers are typically made of materials like house wraps, building paper, or fluid-applied membranes. By preventing water intrusion and air leaks, weather-resistant barriers contribute to the durability and sustainability of the building envelope.
Design Considerations for Energy-Efficient Building Envelopes
When it comes to optimizing energy efficiency in building envelopes, there are key design principles that need to be considered. Factors such as orientation, shading, and air sealing play a crucial role in determining the overall performance of the building envelope and its impact on energy savings.
Orientation
Orientation is a critical design consideration for energy-efficient building envelopes. By strategically positioning the building in relation to the sun's path, designers can maximize natural light and heat gain during the winter months while minimizing heat gain during the summer months.
This can significantly reduce the need for artificial lighting and heating/cooling systems.
Shading
Effective shading strategies can also enhance the energy efficiency of a building envelope. By incorporating features such as overhangs, awnings, or vegetation, designers can control the amount of solar heat entering the building, reducing the need for excessive cooling systems.
Shading elements can also improve occupant comfort and reduce glare, contributing to a more sustainable and energy-efficient design.
Air Sealing
Proper air sealing is essential for preventing the infiltration of outside air and the loss of conditioned air within the building envelope. By sealing gaps, cracks, and penetrations in the envelope, designers can enhance the overall energy performance of the building and improve indoor air quality.
Air sealing also helps maintain consistent temperatures throughout the building, reducing the energy required for heating and cooling.Innovative design solutions, such as passive solar design, green roofs, and high-performance glazing systems, can further enhance energy savings through the building envelope.
By integrating these design considerations and technologies, architects and engineers can create more sustainable and energy-efficient buildings that benefit both the environment and occupants.
Final Review
In conclusion, Building Envelope Enhancements That Save Energy offer a promising avenue for achieving both eco-friendly construction and economic benefits. By optimizing the building envelope through innovative materials and design principles, we pave the way towards a more sustainable built environment.
Top FAQs
What are some common types of building envelope enhancements?
Common types include improved insulation, high-performance windows, and weather-resistant barriers.
How do building envelope enhancements contribute to energy savings?
Enhancements help in minimizing heat transfer, reducing the need for heating and cooling, thus saving energy.
Which materials are commonly used for enhancing the building envelope?
Materials like spray foam insulation, double-glazed windows, and weather-resistant barriers are often used for enhancing the building envelope.
What design considerations are crucial for energy-efficient building envelopes?
Factors like orientation, shading, and air sealing play a significant role in optimizing energy efficiency in building envelopes.